Real-Time Data Sync for Multi-Channel Ecommerce
Instantly sync inventory and orders across channels to prevent overselling and improve reliability with Kafka, Kinesis, Pub/Sub, Redis, or RabbitMQ.

Managing multiple sales channels like your website, Amazon, and eBay requires real-time data updates to avoid inventory issues, overselling, and order errors. Without instant synchronization, businesses risk losing customer trust and operational efficiency.
Here’s why this matters:
- 60% of U.S. online shoppers in 2022 reported abandoning purchases due to out-of-stock issues.
- The real-time database market, worth $8 billion in 2024, is projected to grow to $20 billion by 2034.
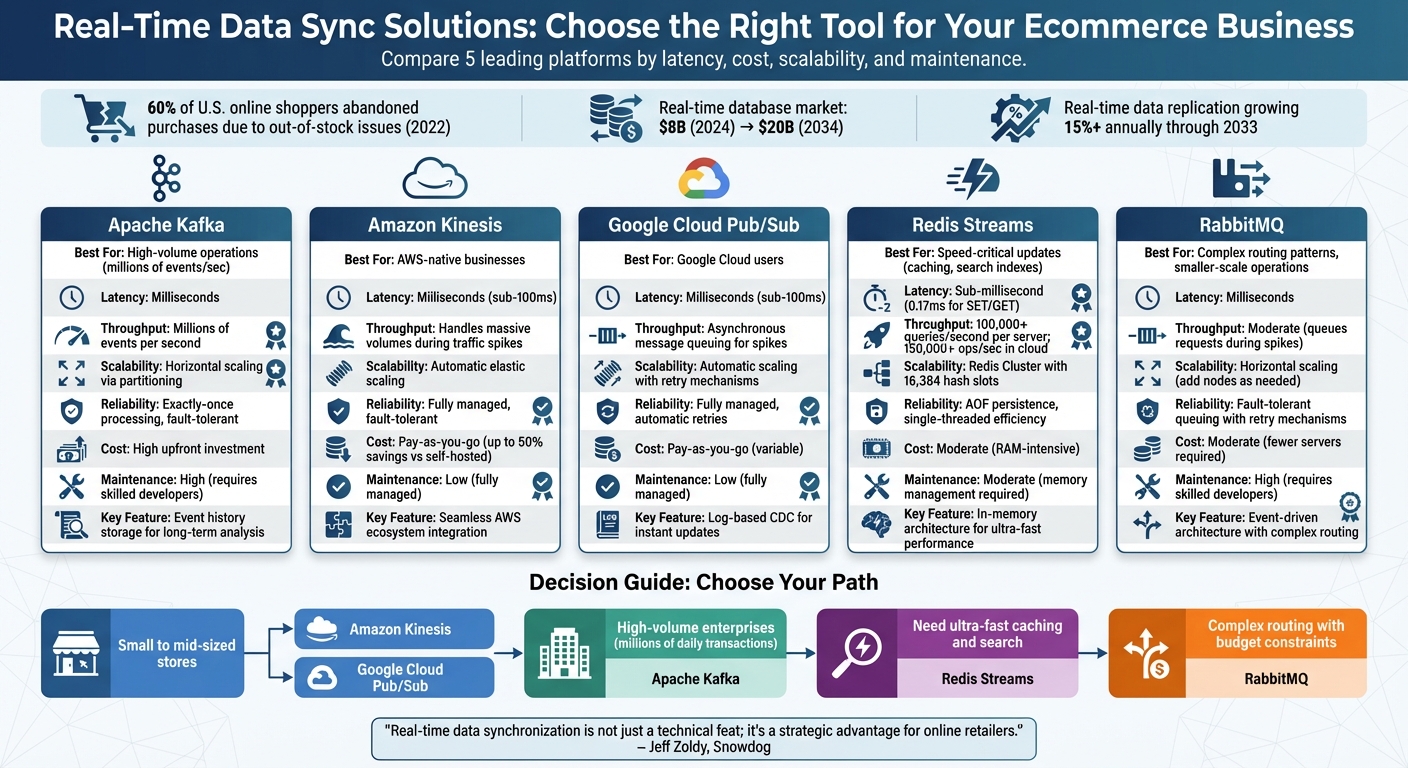
To solve these challenges, businesses are turning to real-time data sync solutions. The best options include Apache Kafka, Amazon Kinesis, Google Cloud Pub/Sub, Redis Streams, and RabbitMQ. Each has unique strengths in latency, scalability, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Key Takeaways:
- Apache Kafka: Best for high-volume operations; handles millions of events per second but requires significant infrastructure.
- Amazon Kinesis: Fully managed, pay-as-you-go solution ideal for businesses using AWS.
- Google Cloud Pub/Sub: Similar to Kinesis but tailored for Google Cloud users.
- Redis Streams: Ultra-fast for caching and search updates, with sub-millisecond latency.
- RabbitMQ: Great for complex routing and smaller-scale operations, though it requires skilled developers.
Quick Comparison:
| Solution | Best For | Latency | Cost | Maintenance Effort |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apache Kafka | High-volume operations | Milliseconds | High upfront | High |
| Amazon Kinesis | AWS-native businesses | Milliseconds | Pay-as-you-go | Low |
| Google Pub/Sub | Google Cloud users | Milliseconds | Pay-as-you-go | Low |
| Redis Streams | Speed-critical updates | Sub-millisecond | Moderate (RAM-heavy) | Moderate |
| RabbitMQ | Smaller-scale, complex routing | Milliseconds | Moderate | High |
Choosing the right tool depends on your transaction volume, technical resources, and growth plans. Real-time systems are no longer optional - they’re essential for staying competitive in ecommerce.
Real-Time Data Sync Solutions Comparison for Ecommerce
How to Automate Your eCommerce Stores Inventory Sync and Management? (2025)
1. Apache Kafka

Apache Kafka operates by tapping into database transaction logs - like MySQL binlogs - to instantly capture every order, inventory adjustment, or customer update as it happens. This method, known as log-based Change Data Capture (CDC), ensures your production database remains unaffected, even when your Shopify or Magento store is processing hundreds of transactions every minute.
Kafka serves as a central hub, linking your ecommerce platform to ERP systems, CRMs, analytics tools, and data warehouses. For example, when a customer purchases the last available item on your website, Kafka streams that inventory update across all your sales channels - like Amazon, eBay, and your mobile app - at the same time. This synchronization helps avoid overselling, even if another customer is about to hit the "buy" button.
"Large-scale Shopify merchants often choose Kafka because order volume can spike rapidly during campaigns like Black Friday, where real-time analytics becomes a competitive advantage." – Lucy, Digital Marketing Specialist
Latency
Kafka can deliver data in just milliseconds. This speed is critical for features like "Buy Online, Pick Up In Store", where customers expect immediate order confirmations and real-time updates on their devices.
Throughput
Handling millions of events per second is Kafka’s strong suit, making it perfect for flash sales or seasonal shopping spikes. By queuing requests during high-traffic periods, it ensures your primary ecommerce database doesn’t get overwhelmed when thousands of customers check out at the same time.
Scalability
Kafka’s horizontal scaling through partitioning allows you to add brokers as your transaction volume grows. This means your system can handle increased demand without needing a complete overhaul.
Reliability
With its exactly-once processing, Kafka ensures precise updates - no duplicate orders, no inventory errors. Plus, its fault-tolerant design keeps your data pipeline running smoothly even if a node goes offline.
Cost
While Kafka requires a higher upfront investment in infrastructure and setup, its performance and dependability make it a worthwhile choice for businesses managing high transaction volumes and complex operations.
2. Amazon Kinesis
Amazon Kinesis is a fully managed service from AWS that streams real-time data changes from your ecommerce databases to all your sales channels. This eliminates the hassle of maintaining your own infrastructure. Whether you're running a Shopify store, managing warehouse operations, or supporting customers, Kinesis integrates seamlessly with your systems to handle real-time data movement, ensuring everything runs smoothly.
Latency
Kinesis processes data changes in mere milliseconds by tapping directly into database transaction logs. This means order updates happen almost instantly. For example, when a customer completes a purchase, the order details are immediately sent to your inventory system, shipping partners, and analytics tools, keeping everything in sync.
Throughput
During high-traffic events like flash sales or holiday shopping sprees, Kinesis manages massive data volumes by using message queues to buffer incoming data. This prevents your database from getting overwhelmed, even when transaction rates skyrocket unexpectedly.
Scalability
As your business grows, Kinesis grows with you. It automatically adjusts its capacity within the AWS ecosystem to match your order volume. This elastic scaling ensures you’re only paying for what you use, making it a flexible solution for businesses of any size.
Cost
Kinesis shifts the financial burden from upfront infrastructure costs to a pay-as-you-go model. This can save you from costly problems like overselling inventory or delays caused by outdated data. That said, it’s important to keep an eye on usage as your transaction volume increases to manage expenses effectively.
3. Google Cloud Pub/Sub
Google Cloud Pub/Sub is a fully managed messaging service that processes database changes - like order_created or inventory_updated - as events. These events trigger immediate updates across channels, helping to avoid issues like overselling during high-demand periods.
Latency
With log-based Change Data Capture (CDC), Pub/Sub delivers updates in just milliseconds. By pulling data directly from transaction logs, it ensures updates happen almost instantly, bypassing the delays that come with batch processing.
Scalability
During traffic surges, Pub/Sub handles the load by queuing and processing messages asynchronously. This system manages spikes in order volume effectively. Plus, features like automatic transaction retries ensure that even if a node goes down, operations continue without a hitch. This makes scaling across multiple sales channels seamless as your business grows.
Cost
While implementing real-time synchronization with Pub/Sub requires upfront investment in development and infrastructure, it cuts down on costs tied to manual updates and data silos. By reducing reconciliation errors and overhead, it streamlines operations and boosts efficiency.
4. Redis Streams
Redis Streams is a lightning-fast, in-memory data store designed to deliver microsecond-level response times. This speed makes it far quicker than traditional disk-based systems and ideal for use cases like acting as a caching layer or message broker. For example, it can help keep inventory and pricing data in sync across platforms like Magento or Adobe Commerce.
Latency
Redis is built for speed. A single server can handle up to 100,000 queries per second, with SET/GET operations clocking in at 0.17 milliseconds. Cloud-based benchmarks push these numbers even higher, exceeding 150,000 read/write operations per second. This means that if a customer buys the last item in stock, the "Sold Out" status updates almost instantly across your website, mobile app, and internal dashboards.
Scalability
Redis operates using a single-threaded model, which eliminates the overhead of context switching and lock contention. Background threads handle tasks like memory management and protocol parsing. For scaling beyond the limits of a single node, Redis Cluster comes into play. It automatically shards data across 16,384 hash slots, enabling the system to handle massive traffic spikes - like those seen during Black Friday sales - without bottlenecks. This setup ensures your data pipeline remains smooth and efficient, even under heavy load.
Reliability
For critical data such as order status updates, Redis offers Append Only File (AOF) persistence with an fsync everysec policy, ensuring data durability. While Redis is optimized for small messages (less than 1MB), larger payloads can introduce delays. To sync Redis with your production database, log-based Change Data Capture (CDC) is a great option. It minimizes performance hits while keeping your data consistent and reliable.
Cost
Redis's in-memory design requires an upfront investment in RAM. However, this approach reduces the need for manual reconciliation and helps eliminate data silos, making it a cost-effective choice in the long run.
5. RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ takes a unique role in handling real-time data events by acting as a distributed message broker. It connects your ecommerce platform to backend systems seamlessly. For instance, when a customer places an order on Shopify, RabbitMQ captures that event and distributes it to systems like analytics, ERP, or fraud detection tools. This event-driven setup allows multiple systems to respond simultaneously without putting undue pressure on your primary database.
Latency
RabbitMQ ensures updates are delivered within milliseconds. This speed is crucial for keeping your operations in sync - like instantly updating a product’s out-of-stock status across your app, marketplace listings, and dashboards. It also handles complex routing patterns effortlessly, directing different types of order data to the right destinations based on customizable rules.
Scalability
When your business grows, RabbitMQ grows with it. Its horizontal scalability lets you add more nodes as your event volume increases. During high-traffic times, such as Black Friday or holiday promotions, RabbitMQ queues requests to manage sudden spikes, ensuring your systems remain stable and responsive.
Reliability
Reliability is a cornerstone of RabbitMQ’s design. It maintains data integrity with fault-tolerant message queuing and retry mechanisms. Even if a downstream service crashes while processing order data, RabbitMQ retains the messages and retries them once the service is back online. This separation between systems ensures that localized issues don’t ripple through your entire infrastructure.
Cost
RabbitMQ is a budget-friendly option for businesses that need dependable real-time synchronization without handling massive data loads. Its setup requires fewer servers, reducing infrastructure costs. However, integrating and maintaining RabbitMQ does demand skilled developers, which could add to your operational expenses.
Advantages and Disadvantages
When diving into multi-channel ecommerce, it's crucial to weigh the strengths and limitations of different solutions. Each option comes with its own set of trade-offs that can impact your operations.
Apache Kafka is a powerhouse for managing millions of events per second while also storing event history for long-term analysis. This makes it perfect for large-scale operations. However, setting it up and maintaining it requires a hefty infrastructure investment.
RabbitMQ shines when you need complex routing to direct various order types to specific systems. It also tends to require fewer servers compared to Kafka. The downside? It needs skilled developers to keep it running smoothly.
Redis Streams is all about speed, with sub-millisecond latency for caching and keeping search indexes updated. This ensures customers always see the latest product information. On the flip side, its in-memory architecture demands careful memory management, and it’s not built for long-term data storage like Kafka.
Amazon Kinesis and Google Cloud Pub/Sub take the hassle out of maintenance since their infrastructure is managed by the cloud provider. These platforms can reduce costs by up to 50% compared to self-hosted solutions, while still delivering sub-100ms latency.
When it comes to architecture, the choice between log-based Change Data Capture (CDC) and query-based polling is critical. Log-based CDC reads database transaction logs passively, meaning it doesn’t add extra load to your production systems. In contrast, query-based polling continuously hits your database with requests, which can be taxing. As Streamkap puts it:
Log-based CDC... puts zero extra workload on your live, production database. It's like listening to a broadcast instead of constantly interrupting the speaker to ask, 'What did you just say?'
Here’s a quick overview of how these solutions compare:
| Solution | Best For | Latency | Infrastructure Cost | Maintenance Effort |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apache Kafka | High-volume operations (millions/sec) | Milliseconds | High | High (skilled devs required) |
| RabbitMQ | Complex routing patterns | Milliseconds | Moderate | High (server management) |
| Redis Streams | Ultra-fast caching and search indexes | Sub-millisecond | Moderate | Moderate (memory tuning) |
| Amazon Kinesis | AWS-native ecosystems | Milliseconds | Variable (pay-per-use) | Low (fully managed) |
| Google Cloud Pub/Sub | GCP-native ecosystems | Milliseconds | Variable (pay-per-use) | Low (fully managed) |
Conclusion
Choosing the right real-time synchronization solution depends on your store's transaction volume, technical capabilities, and growth trajectory. The key factors to consider include latency, reliability, scalability, cost, and throughput - all of which directly impact operational performance.
For small to mid-sized stores, managed cloud services like Amazon Kinesis or Google Cloud Pub/Sub are excellent options. These platforms reduce the technical burden, allowing you to focus on scaling your business rather than managing infrastructure. On the other hand, high-volume enterprises processing millions of daily transactions may benefit from the raw processing power of Apache Kafka, despite its higher infrastructure demands. If rapid growth is your goal, log-based Change Data Capture (CDC) provides near-instant synchronization with minimal impact on production environments.
As Jeff Zoldy from Snowdog aptly states:
Real-time data synchronization is not just a technical feat; it's a strategic advantage for online retailers.
The market trends reinforce this shift toward real-time systems. The global real-time database software market is expected to reach $20 billion by 2034, with real-time data replication software growing at over 15% annually through 2033. This evolution marks a clear departure from traditional batch processing. Today’s ecommerce businesses are embracing event-driven architectures where inventory updates, order changes, and pricing adjustments flow instantly across all platforms.
To thrive in this changing landscape, focus on exactly-once processing to ensure data consistency and prevent errors like dual-writes. Additionally, using a dedicated middleware layer - such as RabbitMQ or Kafka - can help buffer traffic spikes and safeguard your primary database from overload.
FAQs
What are the main advantages of real-time data synchronization in multi-channel ecommerce?
Real-time data synchronization brings a host of benefits to multi-channel ecommerce businesses. One standout advantage is accurate inventory management. By instantly updating stock levels across all sales platforms, it minimizes the chances of overselling or running out of stock. This reliability translates into a better customer experience, as shoppers can confidently rely on product availability.
Another major perk is the boost to operational efficiency. Automated data updates save time and cut down on manual errors, streamlining workflows. Plus, real-time syncing offers a competitive edge by allowing businesses to quickly respond to changes - whether it’s adjusting to store updates, customer behavior, or shifting market trends. In a fast-moving industry, this adaptability can make all the difference.
What should I consider when choosing a real-time data sync solution for my ecommerce business?
When choosing a real-time data sync solution for your ecommerce business, prioritize performance, reliability, and scalability. The platform should be capable of managing your data volume and number of stores while ensuring instant updates to avoid issues like overselling or outdated inventory.
Key features to look for include advanced filtering, automation tools, and seamless integration with essential systems like CRMs or marketing platforms. These features can simplify your processes and improve precision in targeting. Additionally, a solid API and support for scalable architectures - such as change data capture and fault-tolerant systems - are critical for maintaining consistent data across all channels.
Select a solution that aligns with your business size and growth goals. The right choice will provide real-time synchronization, support better decision-making, and help your operations run efficiently.
What are the key differences between Apache Kafka and RabbitMQ for real-time data synchronization?
Apache Kafka and RabbitMQ are two distinct tools, each designed to address different needs in data processing and messaging. Let’s break it down:
Kafka is built for handling massive amounts of real-time data. It operates as a distributed streaming platform, relying on a commit log architecture. This setup allows multiple consumers to access and process data streams independently, making it perfect for tasks like real-time analytics or managing continuous data feeds, such as those in large e-commerce systems.
RabbitMQ, in contrast, is a message broker focused on reliable and flexible communication between applications. It uses a queuing system and supports various messaging protocols. RabbitMQ shines in scenarios where guaranteed delivery, message acknowledgment, and complex routing are essential, such as coordinating microservices or ensuring dependable interactions between different parts of an application.
To sum it up, Kafka is your go-to for high-throughput, real-time data streaming, while RabbitMQ is better suited for dependable, application-to-application messaging in environments like e-commerce.





